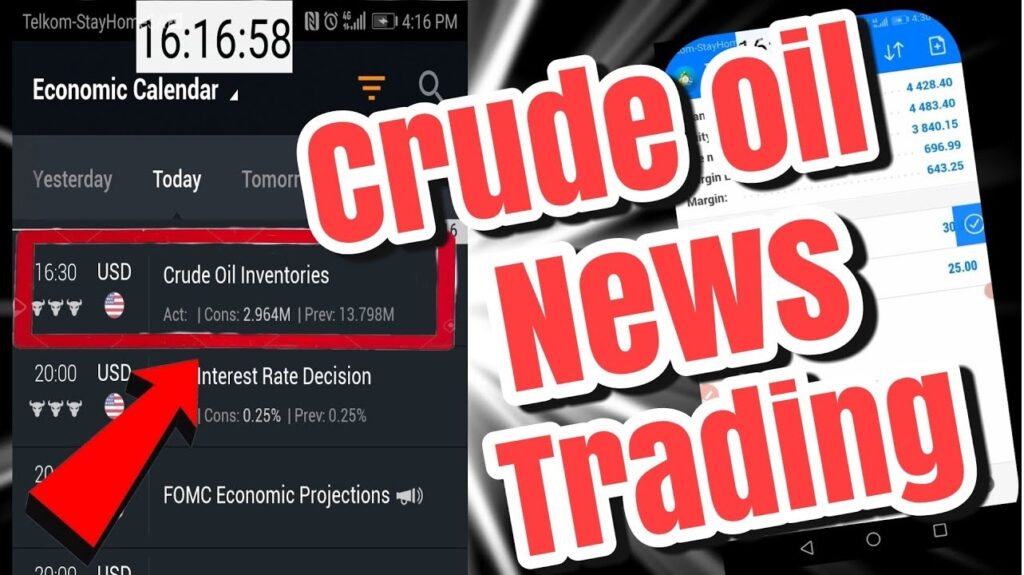
Crude oil inventory is a critical component in the global commodities market, influencing prices and trading strategies across the board. In this article, we’ll explore what crude oil inventory means, how it’s measured, and how traders use this information to predict market trends. We’ll also discuss the key reports that impact crude oil prices, focusing on the API (American Petroleum Institute) and EIA (Energy Information Administration) reports, and how to leverage these reports for successful trading.
What is Crude Oil Inventory?
Crude oil inventory refers to the amount of crude oil that is stored at any given time. It’s a significant indicator of supply levels in the market, which in turn affects crude oil prices. When inventory levels are high, it indicates an oversupply of crude oil, often leading to lower prices due to decreased demand. Conversely, lower inventory levels suggest a higher demand, which can drive up prices.
Key Reports: API and EIA
Every week, two major reports are released that provide insights into crude oil inventory levels—the API and EIA reports. Understanding these reports is crucial for anyone involved in crude oil trading.
- API Report: The American Petroleum Institute releases its inventory data every Tuesday in the U.S., which corresponds to early Wednesday morning in Indian Standard Time (IST). This report is a preliminary indicator of inventory levels, often setting the tone for the market before the official EIA data is released.
- EIA Report: The Energy Information Administration releases its inventory data every Wednesday. In the U.S., this happens in the morning, while in India, the data is available by 8:00 p.m. IST. The EIA report is considered more comprehensive and is closely watched by traders globally.
How Crude Oil Inventory Data Affects Prices
Crude oil inventory data is a strong indicator of market trends. Here’s how the data typically influences prices:
- High Inventory Levels: When the inventory levels reported by API and EIA are higher than expected, it usually signals an oversupply in the market. This surplus leads to lower prices as the demand for crude oil decreases.
- Low Inventory Levels: Conversely, lower-than-expected inventory levels indicate a shortage in supply, which typically results in higher prices due to increased demand.
Trading Strategies Based on Inventory Reports
Crude oil traders closely monitor inventory reports to make informed trading decisions. Here are some common strategies:
1. Trading on API Data
The API report is released at 4:30 p.m. U.S. time, which translates to early Wednesday morning in IST. Since the report comes out when the Indian markets are closed, traders must wait until the market opens at 9:00 a.m. IST to see how prices react to the report.
If the API report indicates lower inventory levels, traders might expect a bullish trend and consider entering a long position when the market opens. However, if the inventory levels are high, a bearish trend might follow, prompting traders to consider short positions.
2. Trading on EIA Data
The EIA report is released at 10:30 a.m. U.S. time (8:00 p.m. IST). Because the Indian market is open at this time, traders can react in real-time.
Due to the report’s comprehensive nature, crude oil often becomes highly volatile around its release. Traders might use a strategy that involves trading with a spread to manage the risk associated with this volatility. For instance, a call spread or a bear put spread can be effective in minimizing losses during volatile periods.
3. Analyzing Price Action
Beyond just looking at the inventory numbers, it’s essential to analyze price action. For example, if the API data shows a decrease in inventory, but the market doesn’t respond with a bullish trend, it could be an indication that traders are awaiting the EIA report for confirmation.
In such cases, traders might adopt a wait-and-see approach, only entering the market after the EIA data is released and a clear trend is established.
Using Historical Data for Better Predictions
Historical data can provide valuable insights into how crude oil prices react to inventory reports. Websites like Investing.com offer detailed historical data for both API and EIA reports, allowing traders to compare forecasted and actual inventory levels. By analyzing this data, traders can refine their strategies and better predict how future reports might impact prices.
For example, if past data shows that the market tends to rally on lower-than-expected EIA inventory levels, traders can plan to enter long positions during similar scenarios in the future.
Conclusion
Crude oil inventory reports are vital tools for traders looking to predict market trends and make informed decisions. By understanding the nuances of the API and EIA reports and analyzing historical data, traders can develop strategies that maximize their chances of success. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting, keeping a close eye on these reports and using them to inform your trading strategies is crucial for navigating the volatile world of crude oil trading.